In the world of Amateur Radio, we have several topics to go over. A lot of newcomers tend to be overwhelmed by what all you need to know. But the simple truth? Learn the basic and go from there. A lot of us tend to focus on the less important subject and we tend to forget the necessary foundation. By means of this web page, I will be going over the basics – the most important subject.
Welcome to the introduction of feed lines.
What is a feed line? What types of feed line are there? These are the common question that anyone newcomer may ask and the most important one. Without feed lines, we would not be able to transmit.
Feed lines (or also known as transmission lines) are lines used to transfer RF energy between a transmitter, receiver or transceiver and antenna.
There are three(3) types of feed lines available for use. They are as follows:
- Coaxial cable: A cable made up of a central conductor surrounded by a layer or insulated material (foam) with a second layer of conducting material and a complete insulation for these components.

Cut out of the inside of a coaxial cable Below we have a complete layout of a coaxial cable.
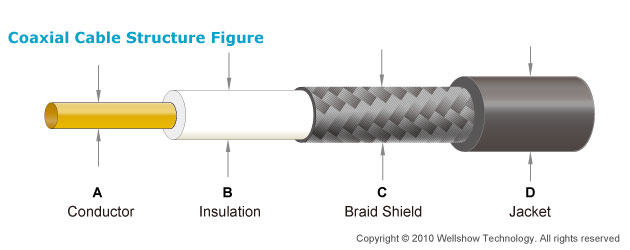
Illustration of interior parts. The inner conductor is either solid copper or stranded copper wire, while the outer conductor is either Aluminum braided wire or a copper sheath. A protective coating covers the conductor. Hardline is coaxial cable in which the outer conductor is solid copper. An example of this type of cable is the LMR 400. Most cables have an impedance of 50 Ohms of 75 Ohms. The purpose of the outer conductor of the cable serves to confine the electromagnetic energy within the cable. Common grades of cable that are used but are not limited to are: RG-174, RG-58, RG-59, RG-8, RG-213, 9913.
- Balanced lines – these feed lines are composed of two conductors that are parallel of each other and at a constant fixed distance apart. Flat TV twin lead have an impedance of 300 Ohms.

TV Twinlead Ladder line is the most commonly used balanced line used in amateur radio, especially in the construction of antennas.
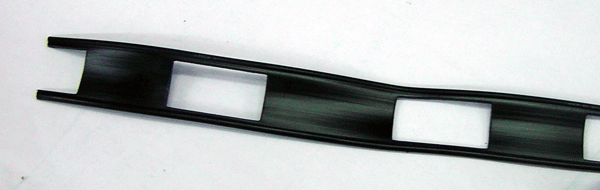
Ladder line It has rectangular sections removed from the center insulator at regular intervals; typically an impedance of either 300 – 450 Ohms. Balanced lines are sensitive to moisture and can interact with nearby objects,
- Wave guides – are used in microwave stations. It is a hollow tube make of conducting material, typically copper, though which electromagnetic energy is transmitted. The tube serves the same purpose as the outer conductor of coaxial cables.

Rectangular made of copper and painted. I hope this fast introduction has served its purpose to immerse you in the world of feed lines deep enough in order to understand the simple terminologies.
